Brain Central Nervous System










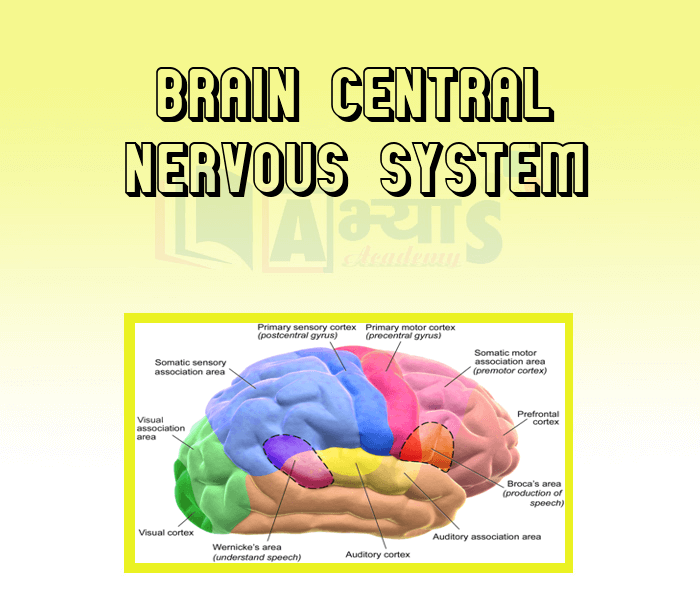
Brain Central Nervous System
The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
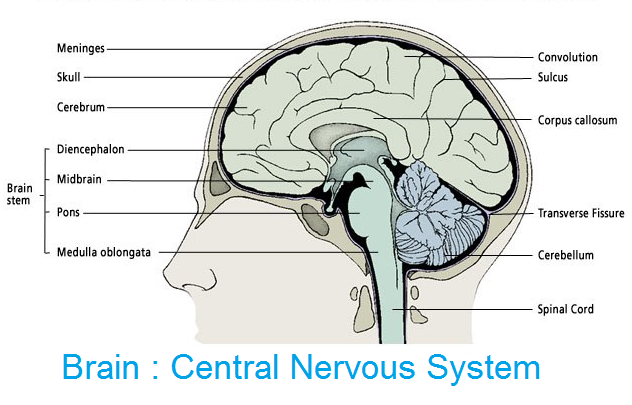
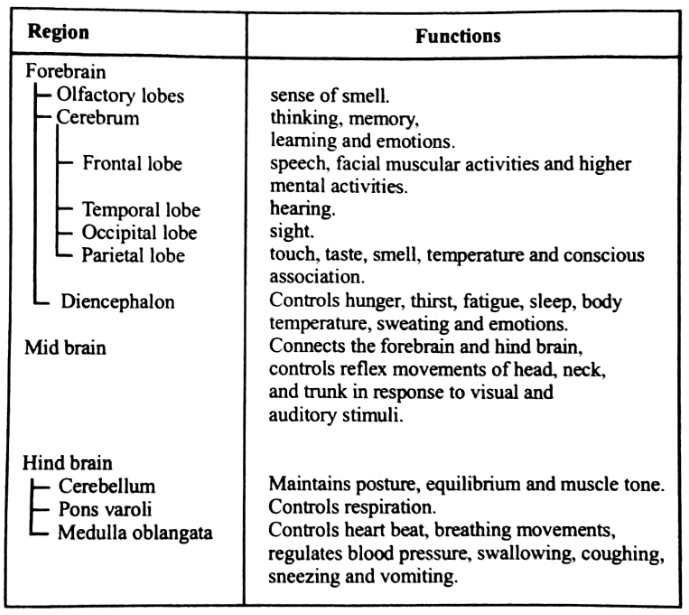
Brain. This is the highest coordinating centre in the body. It is situated in the head region, in the cranial cavity of the skull. It is soft, whitish organ which weighs 1.2 1.4 kg. It forms 98% of the weight of the whole CNS. Brain is surrounded by three protective membranes called meninges. The space between these meninges is filled with cerebrospinal fluid which protects the brain from mechanical shocks. Brain is divisible into three main regions:
(i) Fore brain (ii) Mid brain (iii) Hind brain
(i) Fore brain forms the greatest part of the brain. It consists of three regions:
(A) Olfactory lobes are a pair of club-shaped small structures present below the cerebral hemisphere. Both lobes are widely separated. Each lobe consists of an olfactory bulb and a narrow olfactory stalk. It is the centre of smell.
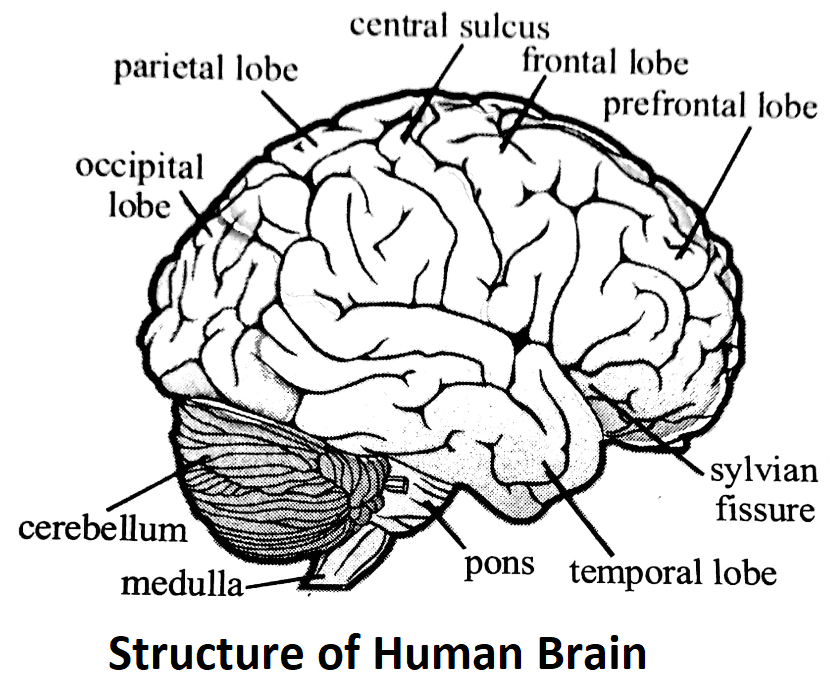
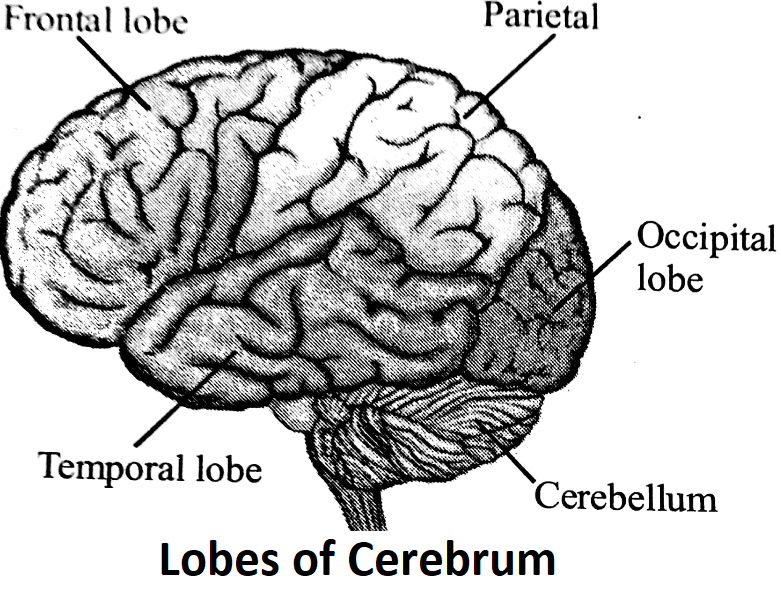
(B) Cerebral hemispheres or cerebrum: forms the largest part of the brain. Cerebrum has two cerebral hemispheres which lie side by side and are separated by a deep cerebral fissure. The surface of cerebral hemisphere has grooves (sulci) and folds (gyri) to accomodate larger number of nerve cells.
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided by three fissures into four lobes:
(a) Frontal lobe on the anterior side. This is the region for speech, facial muscular activities and higher mental activities.
(b) Temporal lobe in the lateral region. This is the region for hearing.
(c) Occipital in the posterior region. This is the region for sight and
(d) Parietal lobe in the middle region. This is the region for touch, taste, temperature and conscious association. Internally each cerebral hemisphere has a fluid-filled cavity called lateral ventricles.
(C) Diencephalon: It is the smallest and unpaired part of brain. It lies on the lower side of cerebrum. Ii has a narrow cavity called third ventricle. Its roof is called epithalamus, side are called thalami and floor is called hypothalamus, Pituitary gland is attached by a stalk to the hypothalamus.
(ii) Mid brain : It extends from the pons to the lower portion of the diencephalon. Mid brain is sub divided into
(a) Optic Lobes (b) Crura Cerebri
(a) Optic lobes : - There are four round solid optic lobes called corpora quadrigemina. Anterior optic lobes are centre of vision and posterior lobes arc for hearing.
(b) Crura cerebri : -These are two ventral bands of nerves connecting diencephalon and medulla oblongata.
Each crura cerebri has two swellings, one in the front called superior colliculi and one at the back called inferior colliculi. The four swellings together are called corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculi are centres for sight reflexes and the inferior colliculi have centres for hearing reflexes.
(iii) Hind brain consists of three parts
(a) Cerebellum is the second Iargest part of the brain. It is made up of two large lateral cerebellar hemispheres and a central vernis. It maintains equilibrium posture and tones of muscles.
(b) Pons : It is located in the centre of brain below the cerebellum. It carries impulses from one hemisphere of cerebellum to other and co-ordinates muscular movements of body.
(c) Medulla oblongata is the posterior most part of the brain which lies below the cerebellum. It continues posteriorly into the spinal cord. It contains a fluid-filled cavity called fourth ventricle. It has centre of respiration, heart beat, vomiting, salivation, sneezing, coughing, swallowing etc.
Functions of different regions of the brain
Brain is a part of | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Brain stem is formed by the union of _____________ | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The control of blood sugar level, osmoregulation and thermoregulation are the function of | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
Abhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.
